NUCLEAR FUEL: OPERATIONAL RISKS AND CHALLENGES
March 09, 2023
A nuclear power plant is a huge water user—consumes about 400 gallons of water Mw/h. It has to compete with several other applications of water supply. Nuclear power plants are susceptible to drought-related shutdowns.
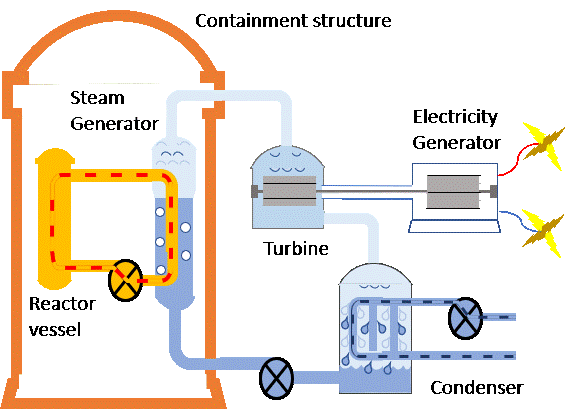
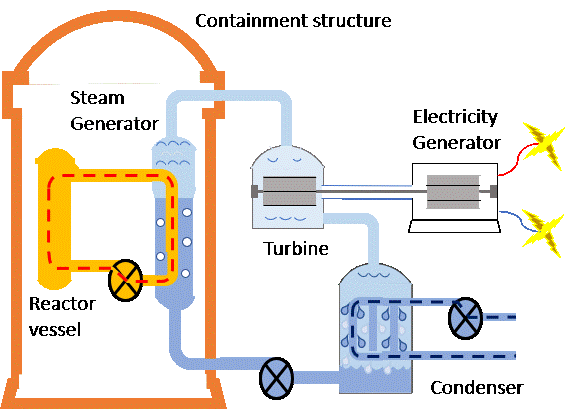
A nuclear reactor is the heat source for the power plant. When each atom splits, such as that of uranium, a large amount of thermal energy is released within a reactor. Water is converted into steam by the heat. The Steam that travels through a turbine makes it spins to convert the thermal energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is used by a generator to produce electricity.
The Estimated levelized cost of energy (the lifetime costs of building, operating, maintaining, and fueling a power plant), for new nuclear plants, is about two times higher compared to estimates for solar, wind, and combined cycle natural gas plants.
Greenhouse gas (GHG) Emissions (g CO2-equivalent kWh)
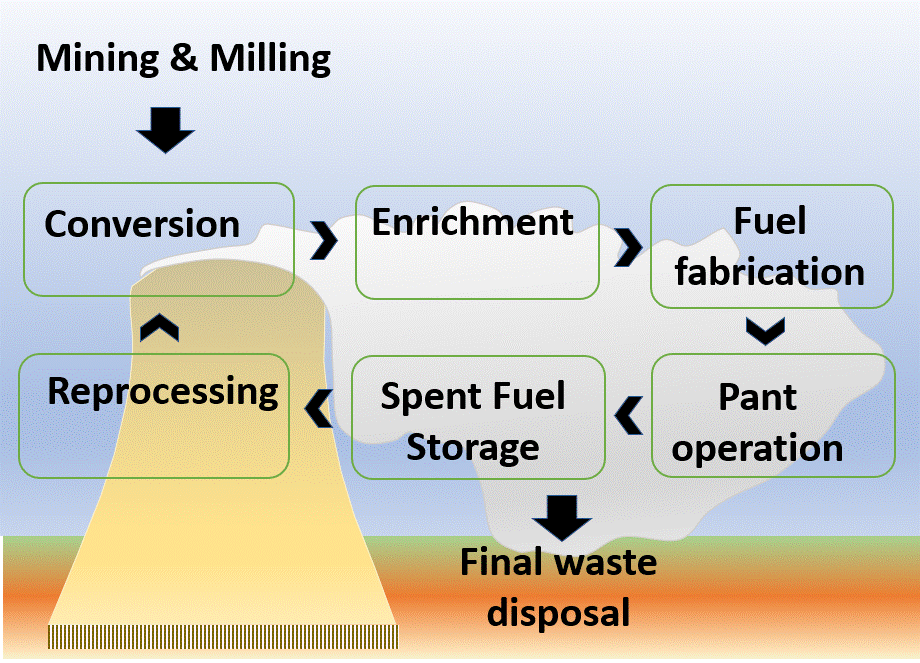
A 1 GW nuclear power plant requires processing 27.6 mt of uranium fuel per annum. 27.6 mt of uranium fuel requires mining 20,000-400,000 mt of ore. The plant has to despose 27.6 mt of highly radioactive spent fuel. The surface of a spent fuel assembly releases 10,000 rem/hr of radiation (a dose of 500 rem is lethal to humans if received all at once), after ten years of use.
People who are exposed to radiation could experience long-term health effects e.g., cancer. If people breathe, eat, or drink something that is contaminated, radioactive materials can get inside the body.
In a 2021 study, investigators found that thyroid tumors in children who were exposed to radiation had higher levels of a particular kind of DNA damage.
References
- Center for Sustainable Systems, University of Michigan. 2021. "Nuclear Energy Factsheet." Pub. No. CSS11-15.
- National Center for Environmental Health, Nuclear Power Plant Accidents, Page last reviewed: December 16, 2019
- United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission, The Pressurized Water Reactor
- Accidents at Nuclear Power Plants and Cancer Risk was originally published by the National Cancer Institute

Home | Contact: info@gazersdigest.com
© 2020-2025 Gazer’s Digest is an information sharing platform. Gazer’s Digest includes topics, thought to be useful for the readers.